Reducing Waste in the Production Line
- Published: February 12, 2024
By Iain Cameron, Marketing Director, Meech International
 Sustainability remains a key talking point within the converting industry, and this makes it more important than ever that sustainable measures are put in place throughout all parts of the production line.
Sustainability remains a key talking point within the converting industry, and this makes it more important than ever that sustainable measures are put in place throughout all parts of the production line.
Static generation is one factor that can pose a significant threat on the quality of packaging while it is produced. If not dealt with correctly and eliminated, it results in nearby and airborne particles being attracted to the surface of a web, hindering the quality of the product, causing print work to potentially appear faded or dirty. Contamination by static on a web can even affect ink performance, repelling it away from the surface of a label.
Static can also pose a health and safety risk to staff. Static usually occurs when a web is moving at high speed. It occurs either via friction when the web makes contact with converting machinery, through “separation” – the unwinding of web rolls — or even via electricity from surrounding machinery.
A web can also become contaminated without the presence of static, when it is moving in high-speed as it drags along ambient air. This creates a boundary layer that can cause debris to become trapped within or beneath the surface of the layer.
Contaminated products, whatever the cause, can result in a high level of packaging products being rendered inadequate and having to be thrown away, affecting the overall production line, increasing waste and slowing down productivity. Fortunately, highly sophisticated static control and cleaning equipment is available that can counter static charges and contamination, ensuring productivity remains at an optimal level.
Web Cleaning
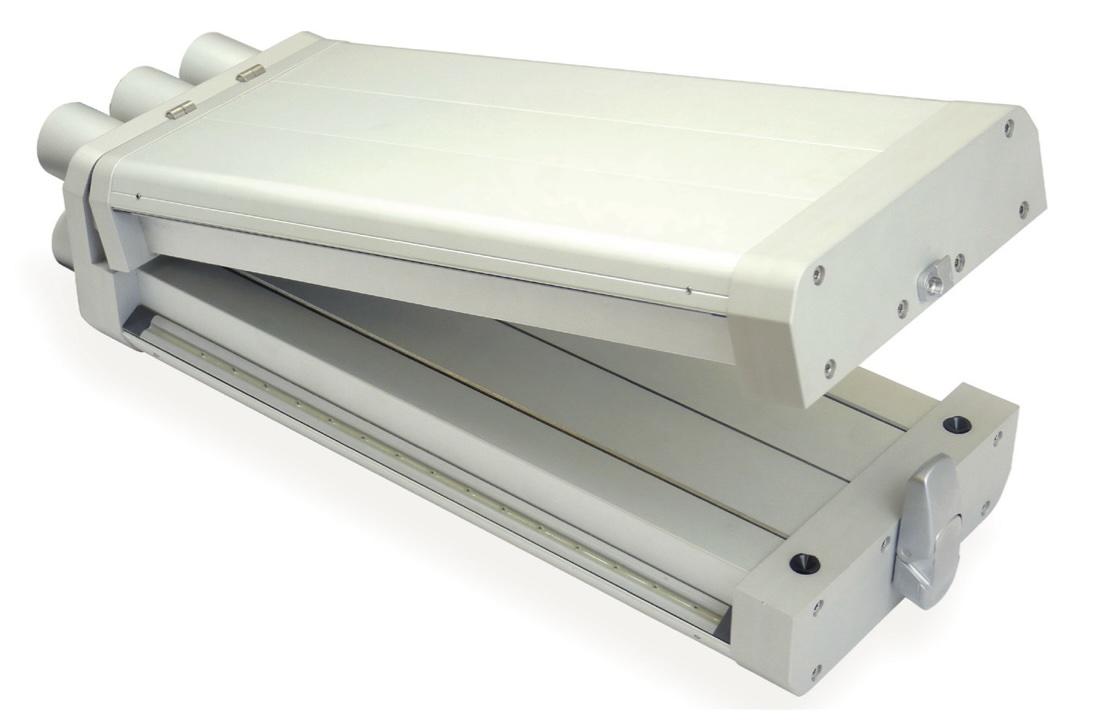 Web cleaners act to effectively resolve contamination issues. Available in two forms, they are highly efficient at removing loose, dry debris from the web’s surface.
Web cleaners act to effectively resolve contamination issues. Available in two forms, they are highly efficient at removing loose, dry debris from the web’s surface.
Web cleaning technology comes in two forms — contact and non-contact. Contact web cleaners are suitable for the narrow web label market. Designed to make contact with the web and break through the boundary layer, they typically use an elastomer and adhesive roller based system, making them ideal for the removal of small particles (as low as 0.5 micron). Other contact systems utilize steel faceplates and brushes to break the boundary layer, although these are less suitable for sensitive substrates.
Non-contact systems have been designed in response to increased demand for compact, high-performance, non-contact web cleaning. These machines typically remove and extract contamination to below 1 micron. Able to clean both sides of the web, they strip the boundary layer of contaminants, capturing them in the airstream and vacuuming them away. Such systems may use positive and negative airflows to break the boundary layer and vacuum away the contamination.
Other forms of non-contact web cleaners use high-velocity rollers, which are typically placed within 1mm of the surface of the web. The roller generates a high speed boundary layer of air. The greater energy of which destroys the boundary layer associated with the incoming web, exposing even the smallest particles to the powerful cleaning force.
Customers should be aware that deciding on the most practical system depends on the web materials being processed, the application, the flexibility required by the converting line and the available budget. While web cleaners can help deter issues surrounding product quality and staff safety, these devices alone will not solve all problems associated with a statically charged web and are most effective when worked in tandem with static control devices.
Static Control
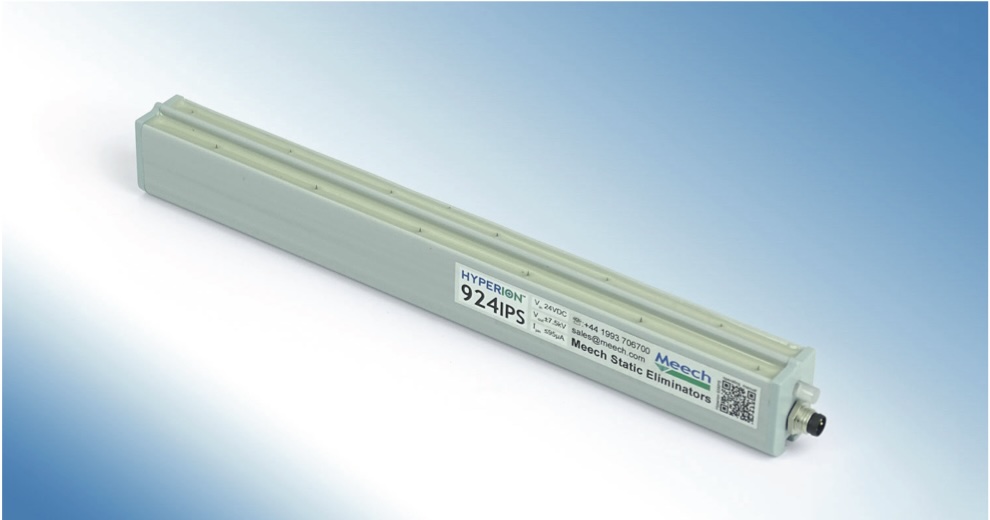 Though web cleaners are very effective at removing contamination, the most effective way to prevent it is to incorporate static control, which can neutralize the charge. This is achieved via the use of an active static control device, such as a DC ionizing bar, which is typically placed before a web cleaner on a production line. It directs positive and negative ions of electricity at the web’s surface, neutralizing any charges present.
Though web cleaners are very effective at removing contamination, the most effective way to prevent it is to incorporate static control, which can neutralize the charge. This is achieved via the use of an active static control device, such as a DC ionizing bar, which is typically placed before a web cleaner on a production line. It directs positive and negative ions of electricity at the web’s surface, neutralizing any charges present.
Most modern ionization bars are available in a range of formats that suit short, medium and long-range applications. Compact in size, these bars are easy to install and with a 15KV pulsed DC output, their performance is unmatched.
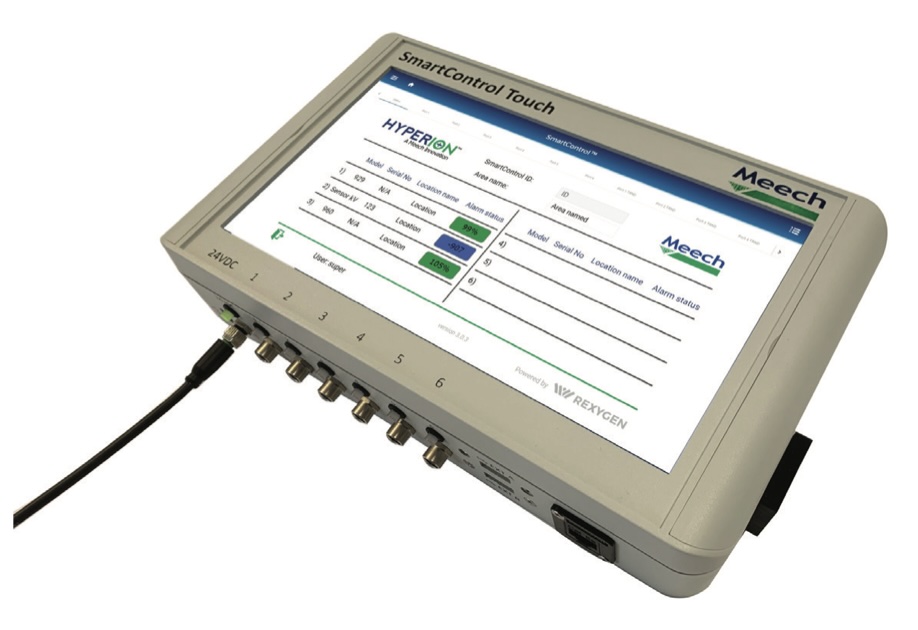
With Industry 4.0 becoming a more prevalent topic within the technology world, static control devices are starting to incorporate automated features. These enable operators to see the performance information of the static control device and control it via a local user-friendly display, such as a mobile phone, tablet, touch screen or monitor. These devices can also be connected to static bar controllers, which alter the level of ionization supplied from the static bar.
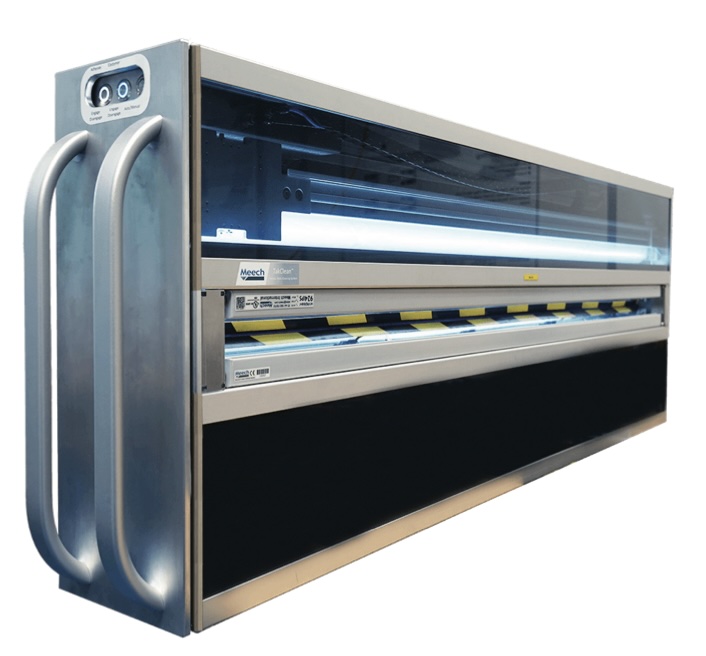 Taking Action
Taking Action
As sustainability remains a growing trend within the industry, web cleaning and static control equipment are must-haves for label and packaging manufacturers to ensure production lines run as effectively as possible, with minimum waste. It reduces waste on the production line, to ultimately avoid increasing carbon footprints and damaging reputation. It is also important to remember that there is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Instead, you must seek a tailor-made solution, ideal for your business.
About the Author
Iain Cameron oversees marketing for Meech International, the UK-headquartered, world-leading manufacturer of Static Control Equipment, Web Cleaning Systems and energy efficient Compressed Air Technology. Meech products are used extensively in a wide range of industries including Packaging, Printing, Converting, Plastics, Food and Drink, Automotive and Pharmaceutical.